Metadata and Docs URLs¶
You can customize several metadata configurations in your FastAPI application.
Metadata for API¶
You can set the following fields that are used in the OpenAPI specification and the automatic API docs UIs:
| Parameter | Type | Description | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
title |
str |
The title of the API. | ||||||||||||
description |
str |
A short description of the API. It can use Markdown. | ||||||||||||
version |
string |
The version of the API. This is the version of your own application, not of OpenAPI. For example 2.5.0. |
||||||||||||
terms_of_service |
str |
A URL to the Terms of Service for the API. If provided, this has to be a URL. | ||||||||||||
contact |
dict |
The contact information for the exposed API. It can contain several fields.
|
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
name | str | The identifying name of the contact person/organization. |
url | str | The URL pointing to the contact information. MUST be in the format of a URL. |
email | str | The email address of the contact person/organization. MUST be in the format of an email address. |
license_infodictlicense_info fields
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
name | str | REQUIRED (if a license_info is set). The license name used for the API. |
url | str | A URL to the license used for the API. MUST be in the format of a URL. |
You can set them as follows:
from fastapi import FastAPI
description = """
ChimichangApp API helps you do awesome stuff. 🚀
## Items
You can **read items**.
## Users
You will be able to:
* **Create users** (_not implemented_).
* **Read users** (_not implemented_).
"""
app = FastAPI(
title="ChimichangApp",
description=description,
version="0.0.1",
terms_of_service="http://example.com/terms/",
contact={
"name": "Deadpoolio the Amazing",
"url": "http://x-force.example.com/contact/",
"email": "dp@x-force.example.com",
},
license_info={
"name": "Apache 2.0",
"url": "https://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0.html",
},
)
@app.get("/items/")
async def read_items():
return [{"name": "Katana"}]
Tip
You can write Markdown in the description field and it will be rendered in the output.
With this configuration, the automatic API docs would look like:
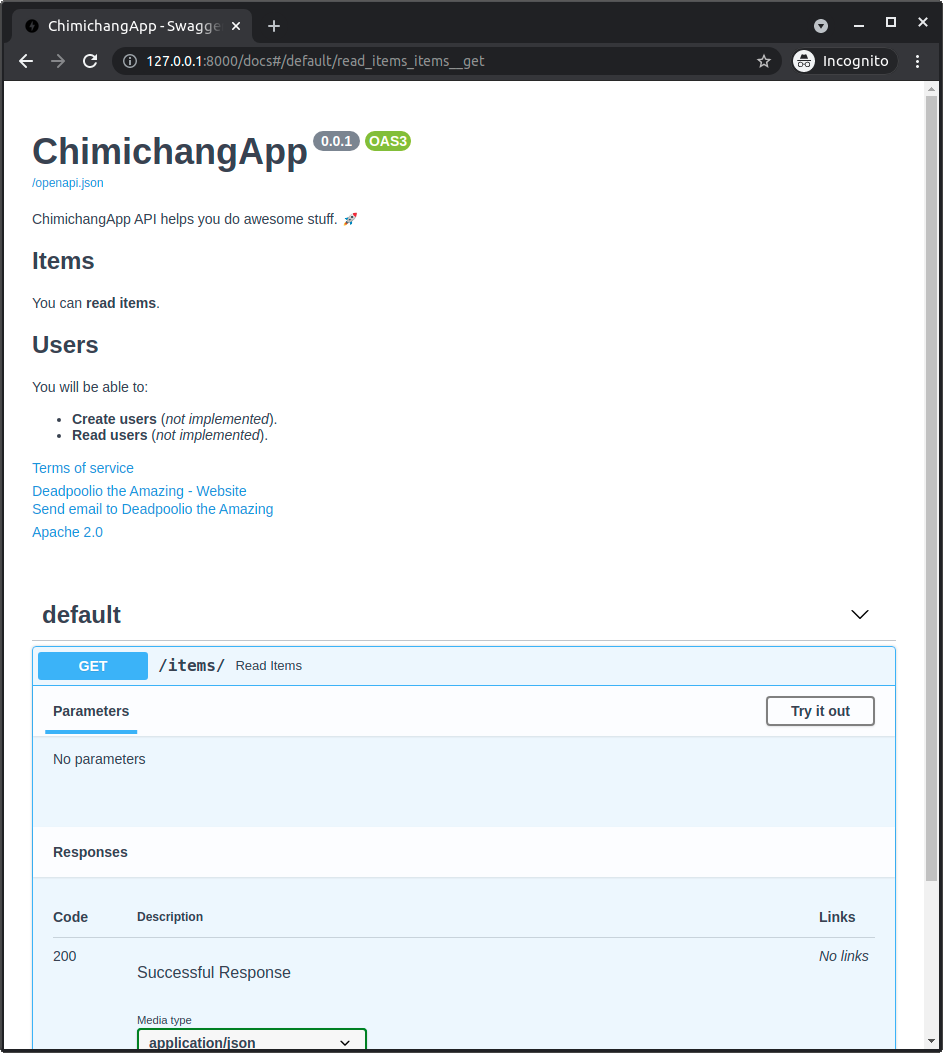
Metadata for tags¶
You can also add additional metadata for the different tags used to group your path operations with the parameter openapi_tags.
It takes a list containing one dictionary for each tag.
Each dictionary can contain:
name(required): astrwith the same tag name you use in thetagsparameter in your path operations andAPIRouters.description: astrwith a short description for the tag. It can have Markdown and will be shown in the docs UI.externalDocs: adictdescribing external documentation with:description: astrwith a short description for the external docs.url(required): astrwith the URL for the external documentation.
Create metadata for tags¶
Let's try that in an example with tags for users and items.
Create metadata for your tags and pass it to the openapi_tags parameter:
from fastapi import FastAPI
tags_metadata = [
{
"name": "users",
"description": "Operations with users. The **login** logic is also here.",
},
{
"name": "items",
"description": "Manage items. So _fancy_ they have their own docs.",
"externalDocs": {
"description": "Items external docs",
"url": "https://fastapi.tiangolo.com/",
},
},
]
app = FastAPI(openapi_tags=tags_metadata)
@app.get("/users/", tags=["users"])
async def get_users():
return [{"name": "Harry"}, {"name": "Ron"}]
@app.get("/items/", tags=["items"])
async def get_items():
return [{"name": "wand"}, {"name": "flying broom"}]
Notice that you can use Markdown inside of the descriptions, for example "login" will be shown in bold (login) and "fancy" will be shown in italics (fancy).
Tip
You don't have to add metadata for all the tags that you use.
Use your tags¶
Use the tags parameter with your path operations (and APIRouters) to assign them to different tags:
from fastapi import FastAPI
tags_metadata = [
{
"name": "users",
"description": "Operations with users. The **login** logic is also here.",
},
{
"name": "items",
"description": "Manage items. So _fancy_ they have their own docs.",
"externalDocs": {
"description": "Items external docs",
"url": "https://fastapi.tiangolo.com/",
},
},
]
app = FastAPI(openapi_tags=tags_metadata)
@app.get("/users/", tags=["users"])
async def get_users():
return [{"name": "Harry"}, {"name": "Ron"}]
@app.get("/items/", tags=["items"])
async def get_items():
return [{"name": "wand"}, {"name": "flying broom"}]
Info
Read more about tags in Path Operation Configuration.
Check the docs¶
Now, if you check the docs, they will show all the additional metadata:
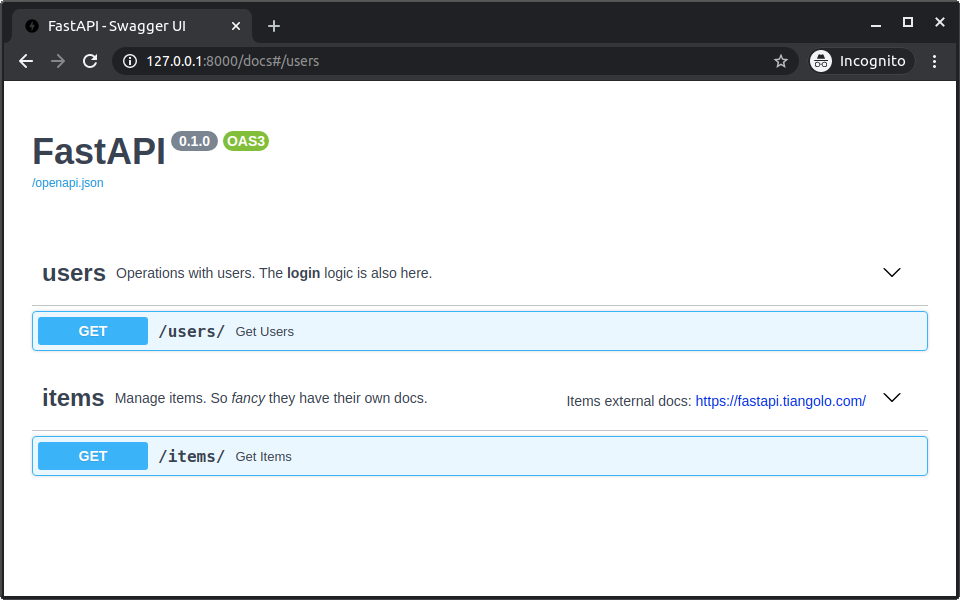
Order of tags¶
The order of each tag metadata dictionary also defines the order shown in the docs UI.
For example, even though users would go after items in alphabetical order, it is shown before them, because we added their metadata as the first dictionary in the list.
OpenAPI URL¶
By default, the OpenAPI schema is served at /openapi.json.
But you can configure it with the parameter openapi_url.
For example, to set it to be served at /api/v1/openapi.json:
from fastapi import FastAPI
app = FastAPI(openapi_url="/api/v1/openapi.json")
@app.get("/items/")
async def read_items():
return [{"name": "Foo"}]
If you want to disable the OpenAPI schema completely you can set openapi_url=None, that will also disable the documentation user interfaces that use it.
Docs URLs¶
You can configure the two documentation user interfaces included:
- Swagger UI: served at
/docs.- You can set its URL with the parameter
docs_url. - You can disable it by setting
docs_url=None.
- You can set its URL with the parameter
- ReDoc: served at
/redoc.- You can set its URL with the parameter
redoc_url. - You can disable it by setting
redoc_url=None.
- You can set its URL with the parameter
For example, to set Swagger UI to be served at /documentation and disable ReDoc:
from fastapi import FastAPI
app = FastAPI(docs_url="/documentation", redoc_url=None)
@app.get("/items/")
async def read_items():
return [{"name": "Foo"}]